The Endocannabinoid System

The Endocannabinoid System
In high school health class or biology, you might have learned about the major organ systems in the human body: skeletal, respiratory, muscular, nervous, etc. However, it is unlikely that you learned about an additional system, the Endocannabinoid System, which is perhaps the most important physiological system involved in establishing and maintaining health in your entire body.

In the 1990’s, scientists discovered endocannabinoids, the natural cannabis-like molecules produced by the human body. Scientists began to realize cannabis exerted its effects, in part, by mimicking our endocannabinoids. It appears the main function of the endocannabinoid system is to maintain bodily homeostasis—biological harmony in response to changes in the environment. Scientific investigation revealed that the endocannabinoid system is incredibly old, having evolved over 500 million years ago. Moreover, it is present in all vertebrates—mammals, bird, reptiles, amphibians, fish, etc, all produce endocannabinoids!
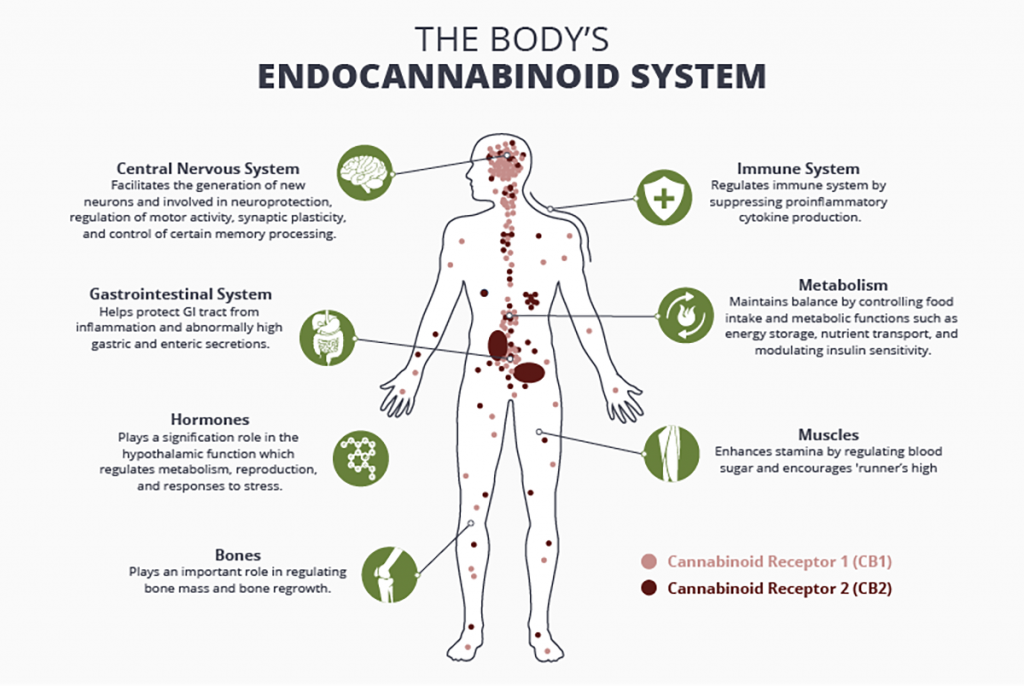
Research initially suggested endocannabinoid receptors were only present in the brain and nerves, but scientists later found that the receptors are present throughout the body, including our skin, immune cells, bone, fat tissue, liver, pancreas, skeletal muscle, heart, blood vessels, kidney, and gastrointestinal tract. We now know the endocannabinoid system is involved in a wide variety of processes, including pain, memory, mood, appetite, stress, sleep, metabolism, immune function, and reproductive function. Endocannabinoids are arguably one of the most widespread and versatile signaling molecules known to man.

There are two main endocannabinoid receptors: CB1 receptors, which are mostly found in the central nervous system and CB2 receptors, which are mostly found in your peripheral nervous system, especially immune cells. Endocannabinoids can bind to either receptor. The effects that result depend on where the receptor is located and which endocannabinoid it binds to.
For example, endocannabinoids might target CB1 receptors in a spinal nerve to relieve pain. Others might bind to a CB2 receptor in your immune cells to signal that your body’s experiencing inflammation, a common sign of auto-immune disorders.

